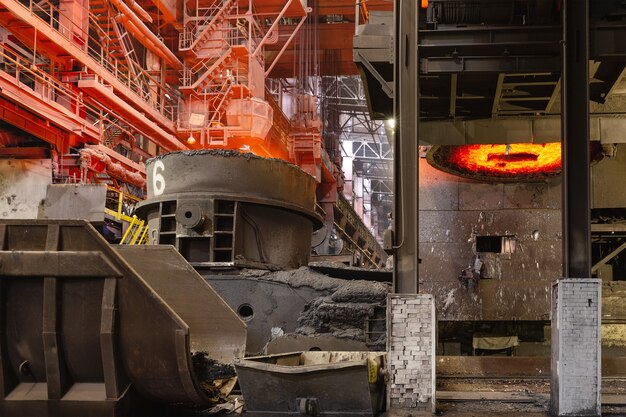
Operating reheating furnaces of rolling mills, especially at steel plants, is not an easy gig. Reheating furnaces are necessary and quite important as they treat steel billets, blooms, and slabs to the appropriate temperature before conducting the next stage of processes. The performance and the reliability of reheating furnaces have a direct influence on the quality of steel and the productivity of the plant in general. However, several issues are associated with the operation of these furnaces, and their mitigation is necessary to obtain optimal efficiency.
Let us look at all issues and their solutions in detail:
Temperature Control
One of the significant problems encountered in steel plants, and generally around the world, is temperature control: the heating furnace of rolling mills should have constant temperature control so as to attain correct mechanical properties through the heating range of this metal. Moreover, if the furnace is extremely hot or too cold, it can give subpar steel with uneven thickness or surface imperfections.
Solution: Modern reheating furnaces use hi-tech methods of temperature control. They comprise sensors as well as automated feedback systems designed to provide consistent heat distribution. Thereby preventing steel overheating or underheating. This equipment needs constant upkeep and calibration to guarantee accuracy.
Energy Consumption
Reheating furnaces consumes a lot of energy and hence may result in high operational costs. Steel plants in Brazil industries are currently hitting rock bottom regarding energy consumption but still maintaining efficiency in production. Poor insulation or old furnace technologies and fluctuation in operational loads are some reasons for energy ineffectiveness.
Solution: Some energy-saving measures that can be applied include improving the furnace’s insulation, utilization of more efficient burners, and waste heat recovery systems. Furthermore, optimal furnace operation through better load management as well as predictive maintenance helps to keep energy costs under control.
Furnace Lifespan and Upkeep
The reheating furnace of rolling mills serves under extreme temperatures, which, after long periods, can lead to the wearing of some parts. The longevity of the furnace relies on several factors, including the quality of the materials used, the frequency of their upkeep, as well as the operational conditions. Improperly maintained furnaces often result in breakdowns, which require huge amounts of money for repair work and downtime.
Solution: Preventive maintenance is the most important way to extend the furnace’s life. Periodic inspections, cleaning, and the replacement of worn-out parts help avoid major breakdowns. Advanced diagnostic tools can also be installed to monitor the performance of the furnace in real time before they become severe enough to result in an actual breakdown.
Emissions Control
Emissions from the reheating furnace, if not well managed, pose a challenge to steel plants. These furnaces usually give off gases of CO2, NOx, and particulate matter, which have adverse environmental impacts. Emissions are an issue that many countries regulate highly for steel plants, and these plants can get charged and their reputation damaged if they fail to meet emission standards.
Solution: The necessary reduction in the released emissions can be achieved by installing advanced technologies like flue gas desulfurization systems, selective catalytic reduction units, as well as electrostatic precipitators. A furnace’s combustion process also needs to be improved in order to increase the completeness of fuel burning so that, consequently, harmful emissions decrease in quantity.
Variability in Raw Materials
The quality of raw materials input in the furnace could vary from one batch to another, especially on billets or slabs. Such variations may affect the consistency of the heating process as well as the quality of the final product yield. Steel plants have to fight such a challenge that can lead to inconsistency among the products coming out of the plant.
Solution: High-quality, consistent raw materials are essential. Furthermore, automation of control systems of the reheating furnace of rolling mills allows for real-time readjustment of heating parameters according to the characteristics of the material coming in. This can thus minimize the effects of variability of raw materials on final product quality.
Furnace Safety
Working on reheat furnaces simply means high temperatures and significant potential safety risk. Explosions, fire, and burning of one’s clothes are just a few potential risks that demand attention.
Solution: For such high-temperature processes, safety precautions can call for the installation of automated shutdown systems, pressure relieving valves, as well as temperature sensors. Along with frequent safety inspections, internal training for operations, like how to do activities properly in a functioning plant, guarantees a safe workplace.
Automation and Control
Automation plays a significant role in the efficient operation of modern steel plants, but relatively complex problems arise during the integration of automation systems in the reheating furnaces of rolling mills. The furnace itself has a complex nature that requires hi-tech control systems, and any failure in the automation system may disrupt the whole production line.
Solution: Investment in reliable, state-of-the-art automation and control systems will be important. Also, training operators to effectively handle automated systems with less chance of error will improve overall performance.
Endnotes
From regulating temperature and energy efficiency to managing pollutants and workers’ safety, running reheating furnaces of rolling mills in steel factories presents several difficulties. Still, many of these problems may be resolved with the required technology, frequent maintenance, and personnel training. Product quality will rise in tandem with operational efficiency development, thereby enabling steel factories to be more sustainable finally.